2025 01/04
What are the Building Codes in Japan? How Does It Affect Buying or Renting a Property?

Japan is an earthquake-prone country. When considering buying or renting a property in Japan, many people are concerned about the New and Old Seismic Codes.
Considering these building codes when choosing a property is especially important in Japan. Additionally, construction methods like "earthquake resistance," " vibration control," and "seismic isolation" should be taken into account when choosing an earthquake-proof building.
We will explain the differences between the "New Seismic Codes" and the "Old Seismic Codes”, as well as the three construction methods. We will also introduce some key points to keep in mind when buying or renting real estate in Japan from the perspective of seismic standards.
The Old Seismic Codes and the New Seismic Codes
The building code is the standard that all buildings must meet to be authorized for construction. In Japan, it tends to be reviewed after every major earthquake. The oldest one is the major amendment of the Urban Building Law (1924) implemented after the Great Kanto Earthquake in 1923.
The Building Standard Law (BSL), established in 1950, stated that all buildings in Japan must comply with earthquake resistance standards. Currently, there are two types of seismic standards: The Old Seismic Codes (1950) and the New Seismic Codes (1981), which is the major amendment of the BSL.
What are the Old Seismic Codes?
The Old Seismic Codes is the standard that was used to be applied to all buildings made before May 31, 1981.
It was based on the idea that all buildings should not collapse during a magnitude 5 earthquake.
What are the New Seismic Codes?
The New Seismic Codes have been applied since June 1, 1981, after the Miyagi earthquake. On June 12, 1978, an earthquake occurred on the coast of the Miyagi Prefecture (the highest magnitude being 5) and about 7,400 houses were completely or partially destroyed in the earthquake. As well as 18 people were killed under fallen concrete-block walls within the Miyagi Prefecture. As a result of this, the BSL was reviewed on June 1, 1981.
This new standard states a new structural standard that a building does not collapse during a magnitude 6 or 7 earthquake.
What is the difference between the two?
There are 2 major differences between the two standards these are
① Earthquake resistance against magnitude 5 earthquakes
② Earthquake resistance against magnitude 6 or 7 earthquakes
On the one hand, the Old Seismic Code states that the security of a building is sufficient if it does not collapse during a magnitude 5 earthquake. However, it is limited because the criteria do not consider the protection against earthquakes over magnitude 6.
On the other hand, the New Seismic Code establishes the following criteria:
◉ Magnitude 5 earthquakes will not damage buildings.
◉ Buildings will not collapse due to magnitude 6 earthquakes or more.
Although the BSL has been revised a few times after the New Seismic Codes were set, its standard of "escaping collapse even in a major earthquake" has not changed.
As the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake occurred, Japan needed to modify the criteria to protect people’s lives and property from major earthquakes.
From this point of view, the New Seismic Codes are a more suitable standard than the Old Seismic Codes for Japan.

Earthquake resistance, vibration control, Seismic isolation
The building codes are legally established to prevent buildings from collapsing in the event of a major earthquake as the minimum standard for safety.
To further decrease the amount of damage caused by an earthquake is through having a different perspective, by considering the location and size of the building, this is called "seismic control," "vibration control," and "seismic isolation.
Moreover, these ideas will be reflected in the building structure.
What is seismic resistance?
Seismic resistance is the concept of how to prevent buildings from collapsing during ground vibrations. To withstand earthquakes adequately, earthquake-resistant construction is built with thick and sturdy pillars.
By comparing the construction methods, the seismic-resistance construction building is more vulnerable to earthquakes out of the three due to it mainly receiving vibrations from the earthquake directly.
What is vibration control?
Vibration control is a method of absorbing vibrations of seismic shaking to prevent buildings from being damaged by earthquakes.
For absorbing seismic energy, vibration-control constructions have a vibration damper. Buildings with a vibration damper are not only resistant to earthquake shaking but also to the vibration from the wind. Therefore, this method tends to be applied to skyscrapers and hotel complexes that are most in contact with stronger winds.
What is seismic isolation?
Seismic isolation is the idea that a device blocks the earthquake vibration before it is transmitted to the building. This is to minimize the damage caused by the shock of the earthquake.
A building with this structure has a seismic isolation layer underneath the building to separate the body of the building and the ground to enable it to reduce the building shaking. Consequently, it prevents the inside of the building from getting damaged such as collapsing furniture, broken windows, and so on.
Therefore, the seismic-isolation structure is seen as the safest structure among the three. However, it does not mean that you must choose a property with a seismic-isolation structure; the effectiveness of these three structures against earthquakes depends on various factors such as the scale of the earthquake and the site condition.

Are all buildings with the New Seismic Codes better?
In recent years, Japanese real estate not only meets the new earthquake-resistant standards but also increasingly uses "vibration control" or "seismic isolation" structures, to help reduce the effects of buildings shaking in the event of an earthquake. Some of them are even built with a structure combining both to maximize security.
This would suggest that old buildings built before 1981 are more vulnerable in comparison to the new ones. We will illustrate the two major earthquakes in Japan to see how the new and old standards work.
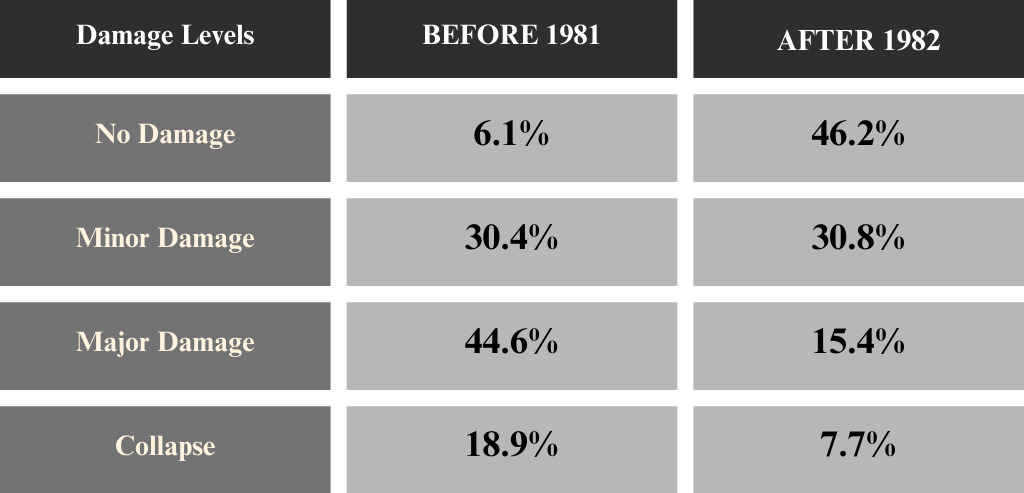
The case of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake (1995)
The Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake (also known as the Kobe earthquake) occurred in the southern Hyogo Prefecture on January 17, 1995. Its maximum magnitude was 7.3 and caused about 580,000 buildings (houses, public buildings, etc.) to become completely or partially destroyed in the earthquake.
The table below shows the damage rate of buildings made before and after 1981:
The case of Kumamoto Earthquake (2016)
The Kumamoto earthquake occurred in both the Kumamoto and Oita prefectures on April 14 2016 with a maximum magnitude of 7.
Based on the data released by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism; the damage rate of wooden buildings under the old and new seismic standards is summarized in the table below:
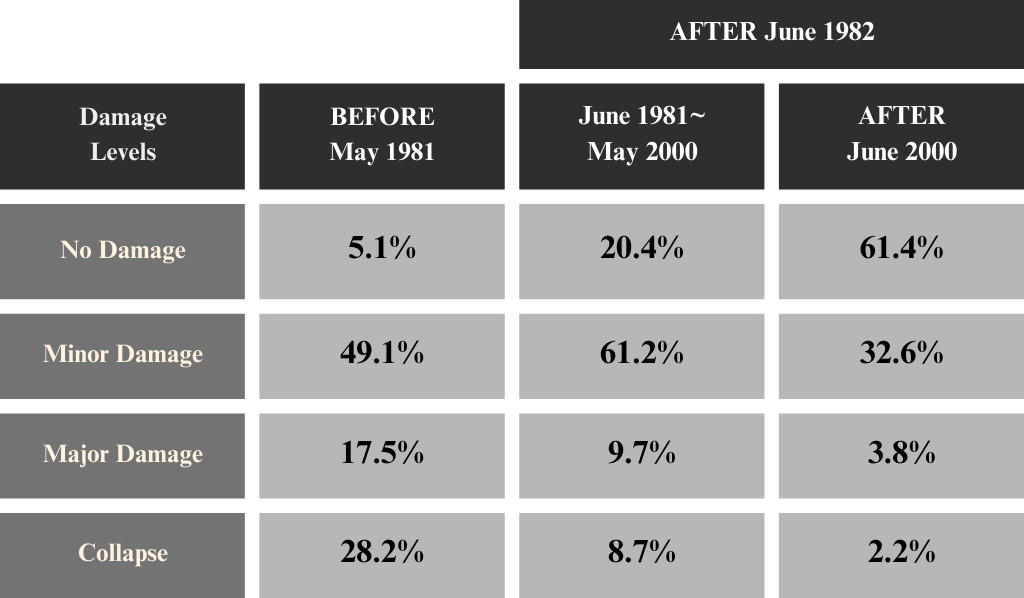
From the two cases, it is obvious that the buildings with the New Seismic Codes tend to have less damage than the ones with the Old Seismic Codes. As for the case of the Kumamoto earthquake, more than 60% of the buildings constructed after June 2000 were undamaged.
In terms of earthquake resistance, it can show how modern buildings are safer than older buildings.
Not all buildings under the old standards are vulnerable.
The data implies a different aspect of considering what a seismic-resistant building is: Not all buildings with the old standards are more vulnerable to earthquakes than those built to the new standards.
As the data shows, about 5-6% of old buildings were not damaged in the case of the two major earthquakes. On the contrary, about 2-9% of buildings with the new standards could not avoid damages.
From these points of view, a building that follows new standards of earthquake resistance does not guarantee that it will avoid damage. In short, a building built before 1981 can still be an option when choosing a property.
How do the building codes affect choosing a property?
Whether you are buying or renting a property, you should always choose a property with earthquake-resistance methods.
In Japan, there is a high probability of major earthquakes. The Cabinet Office estimates a 60% chance in the next 10 years of the occurrence of an oceanic trench-type earthquake with a magnitude over 7.5. In the next 30 years, there is a 99% chance of this earthquake occurring.
Hence you need to be especially careful when choosing a building with the Old Seismic Codes, which were built to resist only earthquakes up to magnitude 5.
The following are some points to check when choosing a property:
① Choose a building with a box frame construction.
Box frame construction (cross-wall construction) is a type of structure in which the load of the building is supported by load-bearing walls instead of columns and beams. The walls (a.k.a. load-bearing walls) are thick and strong concrete walls and are bonded to the floor to support the building.
Box frame construction is stronger against vertical and horizontal forces during earthquakes than a building with a rigid-frame (ramen) construction. In fact, buildings built in a box frame construction caused less damage in the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake.
This building structure is used for low to mid-rise condominiums and buildings with five or fewer floors, as the building strength cannot be adequately maintained at higher levels.
② Choose a building that was built on stable ground.
No matter how much earthquake resistance a building has, if the ground is unstable, the risk of it collapsing increases.
The older the building, the more important it is that the ground is stable.
Below there is useful information to check the stability of a land:
◉ Information on the property’s site conditions provided by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
◉ Liquefaction prediction maps published by the government
◉ Hazard maps published by local governments
③ Choose a building shape that is resistant to earthquakes.
The characteristics of buildings that are most vulnerable to earthquakes even under the new earthquake-proof standards include:
✔ Pilotis (a building shape where the first floor is a space with no walls, like a garage, and the second floor begins as normal where there are residential units).
✔ Properties that are long and narrow.
✔ A property that alternates between two different structural forms.
On the contrary, earthquake-resistant buildings:
・Square-shaped buildings
・Low-rise buildings

How does the Building Codes affect buying a property?
When purchasing real estate, you should acknowledge that there will be differences in the procedures between the New and Old Seismic Codes. In particular, the latter is limited when purchasing.
① Seismic testing
Seismic testing is a process to evaluate the seismic resistance of buildings with the old seismic standard. For some real estate (schools, factories, multi-family residential, etc.), seismic testing is mandatory.
Even if you are buying an old property that is not required to have seismic testing, it is a good idea to have it to reduce future damage costs from earthquakes.
② Mortgage deduction
Mortgage deduction (or mortgage tax reduction) is a tax system in which 1% of the balance of your house mortgage is deducted from income tax or resident tax for 10 years.
This deduction is available for most buildings that meet the new seismic resistance standards. However, it is not available for buildings that meet the old seismic standards.
As an exception, if you can obtain an earthquake resistance certificate, you can receive a mortgage deduction. An earthquake resistance certificate is a document certifying that a building meets the earthquake resistance standards. This is issued by architects or organizations that provide designated verification and inspections for properties. This certificate will be issued once the buildings have been fully assessed.
If the old building is built according to the new seismic standards, the certificate will be issued. This may mean you need to pay lots of money to renovate/repair the buildings to meet the new standards.
③ Tax relief measure
When purchasing real estate, you will need to pay the following taxes:
・“Real estate acquisition tax” (a local tax imposed when land or a house is newly acquired)
・“Registration and license tax” (a national tax imposed when real estate is registered)
・“Property tax” (a local tax imposed on owners with land and buildings)
New earthquake-resistant buildings are eligible for the reduction of these taxes above; old earthquake-resistant buildings are not eligible for that reduction in principle.
④ Low cost-effectiveness
Although old earthquake-proof buildings are affordable, they may cost more than new houses in the long run. For example, when you buy a property, you may need to purchase fire insurance and earthquake insurance; these insurances for an old property are more expensive than the new property. In some cases, you may also have to do seismic retrofitting work on older buildings to make them meet the new standards.

How do the building codes affect renting a property?
For renting, there are fewer points to keep in mind about earthquake resistance in contrast to buying a property.
This is because:
◉ The landlord has the responsibility for conducting seismic testing.
◉ You do not need to live in the same property for a long time.
◉ You do not need to worry about the mortgage deduction.
However, even if you are going to live there for a short time, it is recommended to choose a property with good earthquake resistance.
When you rent an apartment or condominium built under the old earthquake resistance standards, you should at least make sure that the building has undergone an earthquake resistance check.
Owners of condominiums and apartments built under the old earthquake-proof standards are required to have seismic testing (for rental housing that has three or more floors and is the size of 1,000 square meters or more).
Before signing a contract, you will be informed by the “explanation of important points” of whether the property has done the seismic testing or not, so be sure to check this information.

Conclusion
We explained the meanings of the New and Old Codes and how they affect choosing a property. These standards inform you how much a property is possible to resist major earthquakes.
When choosing an older building, you should consider:
※ Seismic testing to ensure your property is secure
※ The amount of related taxes you must pay
※ The cost of repairs and renovations that may occur after seismic testing
For choosing the structure of a building, the site conditions, the building codes, and the highest possible seismic resistance. It is recommended that you consult with an experienced agent since verification requires specialized knowledge and skills.
Reference Links:
https://suumo.jp/article/oyakudachi/oyaku/chukoikkodate/ck_knowhow/c0twn109/
https://web.pref.hyogo.lg.jp/kk42/pa20_000000015.html
https://www.bousai.go.jp/kohou/oshirase/h15/pdf/sankou1-1.pdf
https://www.mlit.go.jp/common/001155087.pdf
https://www.anest.net/study/used-house-taishin201708.html
https://www.taishin-jsda.jp/column.html
https://www.housingstage.jp/guide/funds-mitigation
https://www.nomu.com/tower/guide/005.html
https://hikarinobe.com/contents/earthquake-resistance-standard-14496#midasi4
https://www.propertyagent.co.jp/contents/4214
https://www.mlit.go.jp/jutakukentiku/build/jutakukentiku_house_fr_000054.html